Flux 是什么
Flux 是 Facebook 推出的一种架构思想,专门解决软件的架构问题,和 mvc 类似,但是更加简洁和清晰.
概念
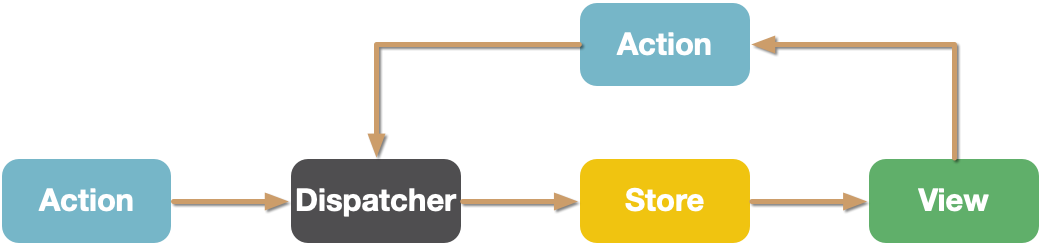
Flux 把一个应用分为四个部分:
- View: 视图层
- Action(动作):视图层发出的消息(比如mouseClick)
- Dispatcher(派发器):用来接收Actions、执行回调函数
- Store(数据层):用来存放应用的状态,一旦发生变动,就提醒Views要更新页面
Flux 最大的特点,就是数据的单向流动性.
以下是 Flux 运行时的步骤:
- 在 view 层触发 Action
- Action 被传递到 Dispatcher
- Dispatcher 要求 store 进行对应的更新
- store 更新,触发 view 改变,从而更新页面
实战
文件目录如下: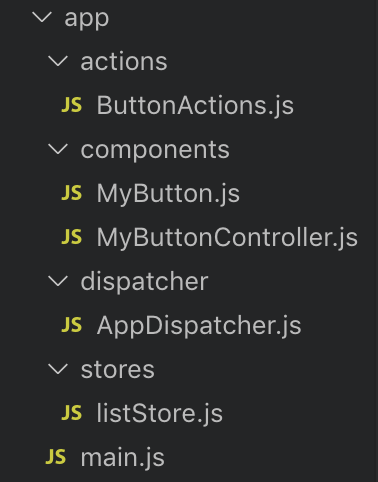
1 | //Mybutton.js |
对 Mybutton.js封装的 MybuttonController.js
1 | import React, {Component} from 'react' |
在我们点击新增按钮后调用createNewItem方法发出一个’ADD_NEW_ITEM’的Action到Dispatcher
接下来我们看看ButtonActions.js
1 | import AppDispatcher from 'app/dispatcher/AppDispatcher' |
这里的addNewItem方法发起了一个actionType为ADD_NEW_ITEM的Action到Dispatcher
然后我们再看AppDispatcher.js
1 | import flux from 'flux' |
最后是ListStore.js1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40import EventEmitter from 'events'
class ListStore extends EventEmitter {
constructor() {
super()
//初始化数据
this.items = []
}
//返回所有数据的方法
getAll() {
return this.items
}
//增加数据的处理函数
addNewItemHandler(text) {
this.items.push(text)
}
//提交变化
emitChange() {
this.emit('change')
}
//监听函数,当有变化时调用注册的回调方法
addChangeListener(callback) {
this.on('change', callback)
}
//remore监听函数
removeChangeListener(callback) {
this.removeListener('change', callback)
}
}
//new一个listStore作为单例暴露给其它模块使用
let listStore = new ListStore()
export default listStore
它负责记录数据和状态并在有变化时改变View
